Lab-grown diamonds, a product that has gained significant attention in the jewelry market in recent years, are gradually winning the favor of consumers with their unique advantages. However, there may still be misunderstandings and questions about Lab-grown diamonds. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of Lab-grown diamonds, helping you better understand and recognize this emerging type of jewelry.
In the following sections, we will explain Lab-grown diamonds in detail from various aspects, including their definition, production process, advantages and disadvantages, identification certificates, and market development. Through this article, we hope to give you a more comprehensive and in-depth understanding of Lab-grown diamonds.
1. Background and Significance of Lab-grown diamonds
1.1 The Romantic Meaning of Diamonds
Diamonds, long considered a token of love, have always carried a romantic meaning. The slogan “heirloom” has made diamonds a dream for countless people. However, as consumers increasingly pursue personal consumption and investment value, the traditional natural diamond market is gradually facing challenges. Issues such as high prices and sustainability have led some consumers to seek alternatives. In this context, lab-grown diamonds have emerged and become a topic of significant interest.
1.2 The concept of laboratory-grown diamonds
Lab-grown diamonds, also known as cultivated diamonds or artificially cultivated diamonds, are diamond crystals that are artificially synthesized in a laboratory by simulating the environment and conditions under which natural diamonds are formed. These diamonds are not mined from the earth’s mineral deposits but are grown in the laboratory through high-tech methods.
The process of cultivating diamonds is accomplished through two main techniques, the high temperature, high pressure method (HPHT) and the chemical vapor deposition (CVD) method.The HPHT technique induces the growth of diamond crystals by exposing a carbon source to the diamond crystal seeds under high temperature and high pressure conditions. This method produces good quality diamonds with high color grades and better clarity. CVD technology, on the other hand, grows diamonds by using a gaseous feedstock under low pressure and high temperature conditions. This method has the advantage of higher clarity and is usually used to produce larger carats.
Cultivated diamonds are identical in composition, structure and appearance to natural diamonds, sharing the same physical, chemical and optical properties. Their transparency, refractive index, dispersion and other characteristics are similar to those of natural diamonds, and therefore they also share the same jewelry characteristics in terms of brilliance, luster, fire and scintillation. Cultivated diamonds and natural diamonds are both genuine diamonds, unlike imitation diamonds such as moissanite (carbon silica) and rhinestones (cubic zirconia).
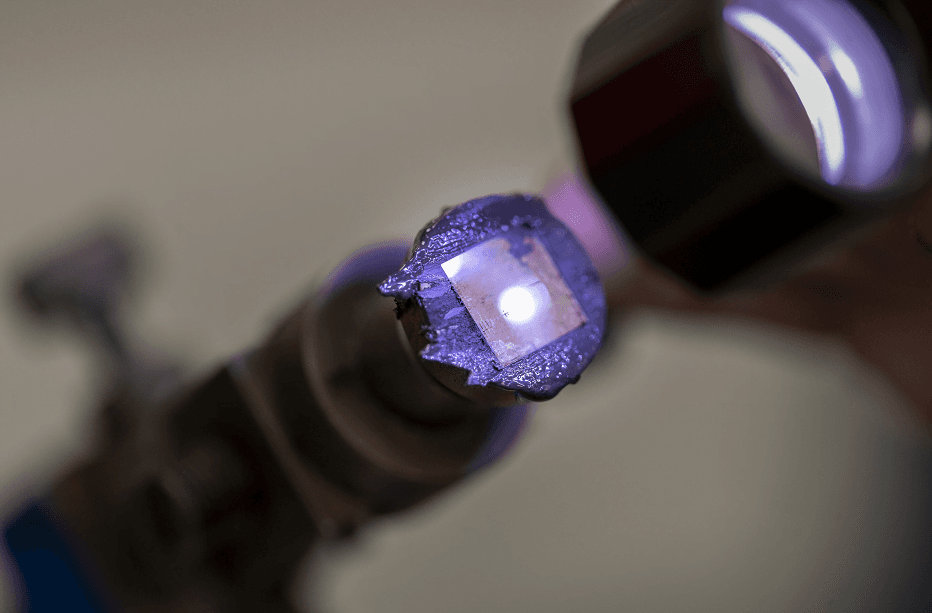

1.3 The Difference and Connection Between Lab-Grown and Natural Diamonds
3.1 Definition and Production Process of Lab-Grown Diamonds
As the name suggests, lab-grown diamonds are artificially synthesized diamonds produced in laboratories. They are created using high-tech equipment and advanced technology to simulate the environment in which natural diamonds form. Although their growth environment is a laboratory rather than deep within the Earth, lab-grown diamonds have the same chemical composition, physical, and optical properties as natural diamonds.
3.2 Formation and Origin of Natural Diamonds
Natural diamonds form under high temperature and high-pressure conditions deep within the Earth and surface only after billions of years of geological changes. The mysterious and unknown formation process of natural diamonds is one reason they are so highly valued.
3.3 Comparison of Physical and Chemical Properties Between Lab-Grown and Natural Diamonds
In terms of physical and chemical properties, lab-grown diamonds are almost indistinguishable from natural diamonds. Both are crystals made of pure carbon, possessing the same crystal structure integrity, transparency, refractive index, and dispersion characteristics. While professionals can distinguish between lab-grown and natural diamonds using high-tech equipment, the naked eye cannot detect any differences in appearance.
3.4 Price Advantage of Lab-Grown Diamonds
Compared to natural diamonds, lab-grown diamonds are more affordable. Their production process can be controlled, generally resulting in higher quality than natural diamonds. Lab-grown diamonds can achieve very high standards of color and clarity, yet their price is only a fraction of that of natural diamonds.
3.5 Environmental and Ethical Benefits of Lab-Grown Diamonds
The production of lab-grown diamonds avoids the environmental impact associated with natural diamond mining and reduces conflicts and issues related to diamond mining. Therefore, lab-grown diamonds are also seen as an environmentally friendly and ethical choice.
3.6 The Connection Between Natural and Lab-Grown Diamonds
Despite the advantages of lab-grown diamonds in terms of production process and price, their connection to natural diamonds is inseparable. The development of lab-grown diamond production technology relies on a deep understanding of natural diamonds. Additionally, the emergence of lab-grown diamonds has impacted the natural diamond market, driving reforms and innovations in the industry.
2. Methods of Cultivating Lab-Grown Diamonds
Lab-grown diamonds are primarily produced through two scientific methods: High-Pressure High-Temperature (HPHT) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). Both methods simulate the natural diamond formation process in a laboratory environment to create high-quality diamonds.
First, let’s explore the High-Pressure High-Temperature (HPHT) method. This technique creates diamonds by simulating the high-pressure and high-temperature conditions found deep within the Earth. Specifically, carbon sources are exposed to a diamond seed under these conditions, encouraging the diamond crystal to grow. The advantage of the HPHT method is that it produces diamonds of excellent quality, with high color grades and better clarity. In terms of quality, HPHT technology offers clear benefits.
Next, the Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) method is another primary technique for growing lab-grown diamonds. This method uses gaseous raw materials under low pressure and high temperature to cultivate diamonds in the lab. Compared to the HPHT method, CVD technology offers higher clarity and is particularly suitable for producing larger carat diamonds. There is no significant price difference between these two methods, allowing consumers to choose the one that best suits their needs.
In summary, both the HPHT and CVD methods can successfully produce high-quality diamonds in the laboratory. These lab-grown diamonds have the same chemical composition, physical properties, and optical characteristics as natural diamonds, making them indistinguishable to the naked eye. This indistinguishability is one of the key reasons why lab-grown diamonds are increasingly popular with consumers.
2.1 (HPHT) VS (CVD) – Key technical differences in laboratory-grown diamonds
2.1.1 HPHT
- The High-Pressure High-Temperature (HPHT) method simulates the high-pressure and high-temperature conditions under which natural diamonds form. This process promotes the growth of carbon sources into diamond crystals on a diamond seed.
2.12 CVD
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is the other main technique used to grow diamonds in laboratories. Unlike the High Pressure High Temperature (HPHT) method, the CVD technique uses a gaseous feedstock at low pressure and high temperatures to grow diamonds in the laboratory. The advantage of this method is that the resulting diamonds are of higher clarity and are usually predominantly large carats (1-5 carats).

3. Advantages and disadvantages of lab-grown vs. natural diamonds
3.1.1 Advantages of Lab-Grown Diamonds
Environmental Benefits: The production process of lab-grown diamonds is relatively environmentally friendly. Unlike mining, which depletes natural resources and causes environmental damage, lab-grown diamond production has a much smaller environmental impact.
Controllable Quality: The production process of lab-grown diamonds can be controlled, resulting in diamonds of excellent quality. The color and clarity can be perfected, matching the quality of the best natural diamonds globally.
Lower Cost: Lab-grown diamonds are typically less expensive than natural diamonds. Since the synthetic production process can be controlled and repeated, the costs are relatively low, giving lab-grown diamonds a competitive price advantage.
Consistent Quality: The production process of lab-grown diamonds allows for precise control over their quality and characteristics. This means manufacturers can produce diamonds with consistent quality, meeting specific requirements and standards. Additionally, different colors and effects can be achieved by altering the impurities added during production.
3.1.2 Disadvantages of Lab-Grown Diamonds
Lack of Scarcity: Natural diamonds are valuable and precious because of their rarity, whereas the supply of lab-grown diamonds is relatively abundant. Large-scale production of lab-grown diamonds may reduce their market scarcity and uniqueness.
Potential Ethical Issues: Although lab-grown diamonds do not involve mining, the raw materials used by manufacturers may come from controversial sources. Ensuring that the raw materials for lab-grown diamonds meet ethical standards is an important issue.
Market Acceptance: Despite the high quality and similar appearance of lab-grown diamonds to natural diamonds, some consumers still prefer natural diamonds. The recognition and acceptance of lab-grown diamonds in the market are still evolving.
3.2 Ethical and Environmental Comparison of the Two Types of Diamonds
3.2.1 Ethical and Environmental Issues of Natural Diamonds
Environmental Impact of Mining: The selection of natural diamond mining sites is very challenging, and the mining methods often involve large machinery, which can harm the Earth’s ecological environment.
Violent Conflicts: The extraction of natural diamonds can involve violent conflicts and exploitation. The process not only damages the environment but also may be associated with bloody disputes.
3.2.2 Ethical and Environmental Advantages of Lab-Grown Diamonds
No Mining Activities: The production of lab-grown diamonds does not involve mining activities, so it does not cause the environmental destruction associated with mining.
Ethical Standards: The raw materials used in the production of lab-grown diamonds come from secure and ethical sources, ensuring they meet ethical standards.
4. Factors affecting the quality of lab-grown diamonds – how to tell the difference between good and bad lab-grown diamonds
4.1 Production Technology
The main production technologies for lab-grown diamonds are High-Pressure High-Temperature (HPHT) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). Each method has its pros and cons, significantly impacting the diamond’s quality. For example, HPHT can produce higher-quality diamonds with better color grades and clarity, while CVD offers higher clarity and is particularly suited for producing larger carat diamonds.
4.2 Growth Environment
Lab-grown diamonds are created in a laboratory setting that simulates the natural growth environment of diamonds, including temperature, pressure, and carbon sources. Minor differences in these growth conditions can result in variations in diamond quality.
4.3 Seed Crystal Quality
The seed crystal is the starting point for diamond growth, and its quality directly affects the final diamond’s quality. High-quality seed crystals promote the growth of more perfect diamond crystals.
4.4 Production Time
The production time for lab-grown diamonds is relatively long, typically ranging from a few weeks to several months. Extended production times can increase the difficulty of quality control, potentially affecting the diamond’s quality.
4.5 Post-Processing
After the growth process is complete, lab-grown diamonds require cutting, polishing, and other post-processing treatments. The precision and professionalism of these processes also impact the diamond’s quality.
4.6 Testing and Certification
Lab-grown diamonds need to be evaluated by professional testing and certification organizations. At Oveela Jewelry Shop, we provide IGI certification for lab-grown diamonds of 1 carat and above, ensuring quality and authenticity.
In summary, various factors influence the quality of lab-grown diamonds, from production technology to post-processing, and testing and certification. For consumers, the best and easiest way to choose a lab-grown diamond is to refer to the 4Cs standard (cut, color, clarity, and carat weight).
-
Unique Cushion Cut Diamond Engagement Ring – Vintage Yellow Gold Bridal Wedding Ring
$852.00Original price was: $852.00.$660.00Current price is: $660.00. -
1.5 Carat Oval Cut Lab Diamond Engagement Ring – Vintage White Gold Nature-Inspired Unique Diamond Bridal Promise Ring
$985.00Original price was: $985.00.$785.00Current price is: $785.00. -
2 Carat Oval Cut Lab Diamond Engagement Ring – 14K Yellow Gold
$1,310.00Original price was: $1,310.00.$760.00Current price is: $760.00. -
1 Carat Round Cut Lab Diamond Engagement Ring – Vintage Solid Yellow Gold Bridal Wedding Anniversary Gift
$718.00Original price was: $718.00.$680.00Current price is: $680.00. -
1 Carat Heart Shaped Lab-Grown Diamond Engagement Ring – Vintage 14K Rose Gold Delicate Bridal Wedding Gift
$878.00Original price was: $878.00.$732.00Current price is: $732.00.
Summary
Lab-grown diamonds are highly regarded for their lower environmental and social impacts. They offer numerous advantages that merit our attention. At Oveela, we emphasize sustainable development and make efforts in environmental protection and social responsibility, and lab-grown diamonds align perfectly with this trend.
By adopting and promoting lab-grown diamonds, we aim to help consumers truly understand, appreciate, and experience lab-grown diamonds. We want them to recognize, as we do, the significance of lab-grown diamonds.
The future jewelry market will reflect diversity, sustainability, and innovation, and lab-grown diamonds will undoubtedly become a focal point in our jewelry design and production. If you have any questions while selecting and purchasing lab-grown diamonds, please feel free to contact us. We will provide answers to all your inquiries.














